Table of contents
Browse categories
Top authors
What is Durability Testing and Why Should You Do It?

February 11, 2025
Durability testing is a process whereby products are pushed to their limits, to ensure that they will perform as intended under real-world operating conditions.
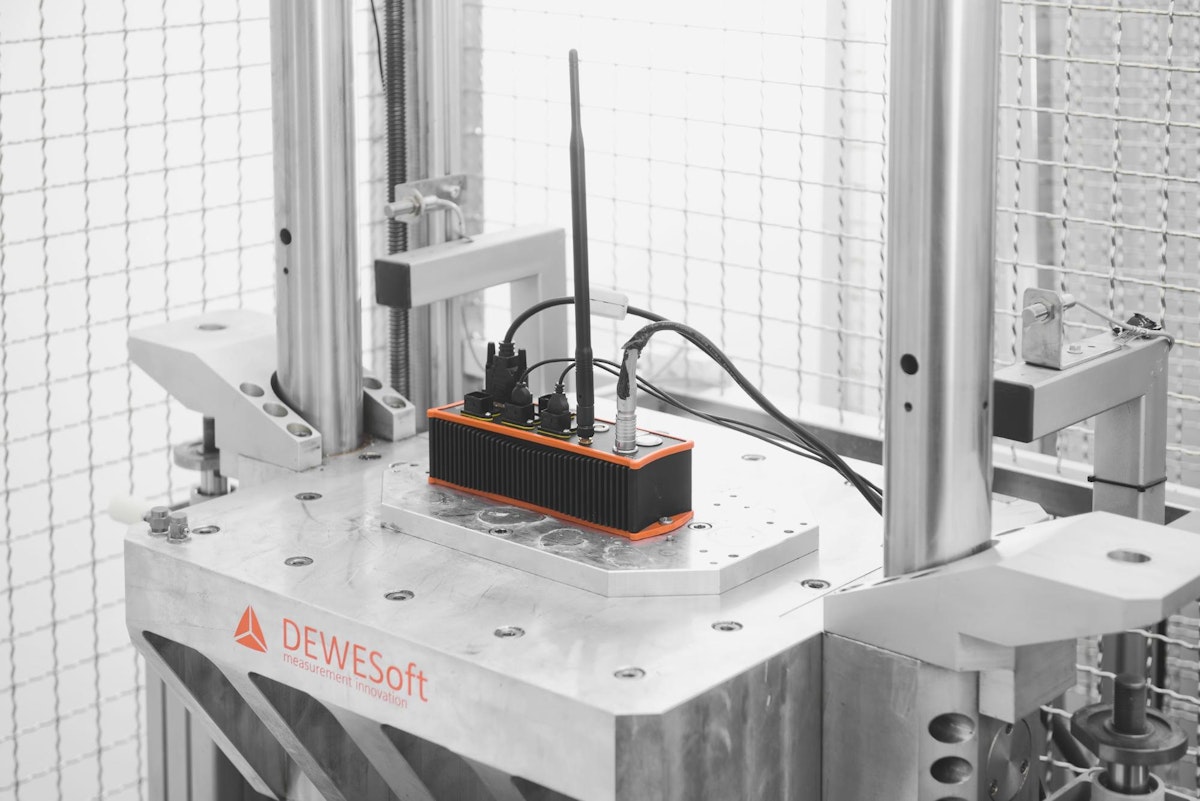

What is durability testing?
Also called “reliability testing” and “endurance testing,” durability testing is a systematic process used to assess the lifespan, strength, and performance of a product under a variety of conditions. Durability testing replicates the wear and tear that products experience during their intended lifespans in a shorter timeframe.
Why do we need durability testing?
A perfect example of why we need durability testing is a car door. How many times will a door be opened and closed during 10, 20, or even 30 years? Using a servo motor in a test chamber a car door can be opened and closed thousands of times in a matter of days. Different amounts of force can be used to simulate slamming and other conditions.
Durability testing helps engineers identify design errors, structural defects, material weaknesses, and manufacturing errors that may cause the hinges, latch, handle, or any part of the door to fail. In addition, the accelerated nature of some durability tests provides this critical information in hours or days instead of weeks or years. Identifying flaws and correcting them before a product has been produced allows manufacturers to provide better quality and more reliable products.
Durability testing across diverse industries
Durability testing is important not only for car makers but across virtually all industries, including aerospace, consumer goods, electronics, industrial machinery, and many more. Let’s examine these in more detail:
Automotive industry
“Road Load” testing is well-known to vehicle manufacturers of all types. Data acquisition (DAQ) instruments collect sensor data from a vehicle driving either test track or real streets.
This data is then fed into a “four poster” testbench equipped with servo motors that re-create the forces and vibrations of the real drive. With a road load system, a vehicle can be subjected to the equivalent of thousands of hours of actual driving in a short time.
Temperature and extreme environmental condition testing is performed on vehicles of all kinds. These include both, climatic chambers as well as with real drive testing in both scorching hot and freezing cold locations around the world. High and low-altitude testing is also performed to ensure that cars, trucks, and motorcycles will operate properly no matter where on earth they are used.
Hundreds of individual components and systems are subjected to durability tests, such as the car door example mentioned earlier. Corrosion resistance, structural integrity, component test, and water ingress are additional examples. Durability testing ensures that vehicles of all types can endure years of operation without failure.

Aerospace industry
Aircraft components undergo extensive durability testing, including wings, control surfaces, engines, landing gear, servo motors, and avionics systems. The goal is to verify that these components can withstand the stresses associated with takeoff, landing, and turbulence, as well as normal and extreme flight conditions.
A perfect example is the durability testing of aircraft landing gear. Parker Hannifin’s Wheel and Brake division in Ohio subjects their wheels and landing gear to dynamometer, combined load, endurance, and roll testing to quantify how they will handle the stresses of actual use.
Read the case study:
Whole aircraft as well as components and subsystems are commonly subjected to environmental extremes such as hot and cold testing in climatic chambers.
Consumer electronics
If you dropped your smartphone onto a hard surface ten years ago there is a good chance that it broke. But today, thanks to durability testing and the improvements in materials and mechanical design, it’s far more likely to survive the impact. Drop testing, environmental testing, and even water submersion are all durability tests that are performed on consumer electronic products like smartphones, notebook computers, and more.
Consumer electronics durability tests also include vibration testing, environmental testing (temperature and humidity), mechanical stress/strain testing, abrasion testing, controls testing of buttons and switches, touchscreen testing, battery and charging cycle testing, water/dust testing, and connector/port testing.
Industrial machinery
Durability testing is crucial in developing industrial machinery like manufacturing equipment, construction machinery, material handling, CNC machines, gearboxes, pumps, robots, machine tools, packaging, electrical power generation components, chemical processing equipment, and more. Rigorous testing ensures that these machines will work reliably under heavy loads and around-the-clock usage.
How is durability testing performed?
Durability testing involves a range of tests that simulate real-world conditions and scenarios. The choice of tests is driven by the nature of the product as well as the industry for which it is intended. Here are the major types of durability tests that are employed:
Vibration testing
Products are subjected to controlled vibrations to simulate the effects of transportation or continuous usage. This is especially critical for products with moving parts, such as automotive components or electronic devices.
Thermal cycling
Thermal cycling involves exposing products to extreme temperature variations. This helps identify how materials and components respond to temperature changes, ensuring that products remain reliable in different climates.
Drop and impact testing
Commonly used in the consumer electronics industry, drop and impact testing assesses a product's resilience to accidental drops and impacts. This is crucial for devices like smartphones and laptops that are prone to accidental falls. But it’s not only consumer products that need to survive impacts, of course. Products of all sizes across all industries are drop-tested to verify their failure points, like the very large container in the example below.
Accelerated aging tests
It would be impractical to test a product intended to last 20 years for literally that much time. Therefore, exposing products to conditions that age them at an accelerated rate helps predict how they will perform over the long term, in much less time.
Humidity and environmental testing
Products are subjected to high humidity levels to evaluate their resistance to corrosion, rust, and other possible degradations caused by environmental conditions.
Immersion testing
Products that are intended to be water-proof must be tested to ensure that they meet their specifications. There is a range of IP specifications that define a product’s resistance to water, other liquids, smoke, dust, and other particulate matter, and for how long the product should resist incursion.
What are the benefits of durability testing?
The main purpose of durability testing is to improve product quality and reliability, but there are other benefits as well. Here are a few:
Early defect detection
Durability testing allows manufacturers to identify defects or weaknesses early in the development process. Addressing these issues before mass production saves significant costs from product recalls or costly in-warranty repairs.
Optimized design
Insights gained from durability testing feedback into next-generation product designs, including with choice of materials and optimized manufacturing processes.
Customer satisfaction
Products that undergo thorough durability testing are more likely to meet or exceed customer expectations. Customer satisfaction and loyalty are good for business.
Regulatory compliance
Durability testing helps ensure that products comply with industry-specific regulations and standards. Various industries require adherence to national and international norms, regulations, and standards.
Longer product life
The combination of durability testing and quality assurance invariably leads to better products that last longer and promote customer satisfaction.
Competitive analysis
It only makes sense for companies to test their competitors’ products, to see how they compare and see how they have solved various challenges.
What are the challenges of durability testing?
Durability testing comes with its own set of challenges, including:
Simulation realism
Ensuring that durability testing conditions closely mimic real-world conditions is essential to obtaining meaningful results.
Accelerated timeframes
Durability testing can be time-consuming, especially when trying to simulate long-term usage. Accelerated testing methods help to mitigate this challenge, but they require careful calibration to reflect real-world conditions accurately.
Costs and resources
Setting up comprehensive durability testing facilities and conducting tests is expensive and consumes resources. Finding the ideal ratio of cost to benefits is essential for every manufacturer.
Variability in usage patterns
Predicting how consumers will use products over time is not an exact science. Changing usage patterns brings uncertainties into durability testing.
What are the best practices for durability testing?
Adherence to best practices maximizes the effectiveness of durability testing. For example:
Define clear testing objectives
Clearly defining a product’s expected lifespan and usage conditions is essential when choosing the durability testing protocols that will be performed.
Achieve realistic simulations
Test simulations must be as realistic as possible to provide meaningful results. The more realistic testing conditions are, the more accurate the results will be.
Regular test iterations
Test iterations should be conducted regularly, especially during the product development phase. Iterative testing promotes continuous improvements and refinements.
Team collaborations
Collaboration among design, engineering, and testing teams is essential. Clear communication across product development, engineering, and manufacturing disciplines leads to actionable improvements.
What are the trends in durability testing?
Durability testing evolves as fast as technology itself. Here are some recent trends to be aware of:
Use of digital twins
“Digital twins” are virtual instances of products, allowing for software-based simulations. This can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of durability testing and allows testing in a virtual environment in ways that may not be practical or even possible to perform physically.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics is the use of statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and data analysis to predict the behavior, performance, and lifespan of products and components in the real world.
IoT integration
By integrating IoT (Internet of Things) devices, sensors, and connectivity solutions into a testing infrastructure, engineers can collect real-time data, monitor test conditions remotely, and analyze performance metrics to improve product reliability and durability.
FAQ
What is durability testing?
Durability testing is a process of evaluating a product's ability to withstand the conditions of its intended use over an extended period. This type of testing assesses the product's longevity and resistance to wear, fatigue, and environmental factors.Why is durability testing important?
Durability testing is crucial to ensure that a product is reliable, safe, and capable of performing over time. It helps manufacturers identify potential weaknesses in design and materials, leading to improvements and compliance with quality and safety standards.What types of products undergo durability testing?
Almost any product can undergo durability testing, but it's particularly important for items subject to continuous or heavy use, such as automotive parts, consumer electronics, building materials, and industrial machinery.How is durability testing conducted?
Durability tests simulate the expected lifespan of a product under accelerated conditions. This may include stress tests, fatigue tests, environmental exposure tests, and usage simulations.What are common methods used in durability testing?
Common methods include accelerated life testing, fatigue testing, wear and tear testing, environmental testing (like temperature and humidity extremes), and load testing.How long does durability testing take?
The duration of durability testing varies based on the product, the nature of the test, and the lifespan the product is expected to have. Accelerated testing methods are used to simulate longer periods in a shorter span.Is durability testing the same as quality testing?
While both are related to product reliability, durability testing specifically focuses on the product's lifespan and long-term use. In contrast, quality testing often assesses broader aspects of product performance and safety.Can durability testing be customized for specific products?
Yes, durability tests are often customized to reflect the specific conditions and stress a product will face during its actual use.Are there standards for durability testing?
Yes, various industry-specific standards guide durability testing. These standards ensure that testing is consistent and comparable across similar products.How do companies use the results from durability testing?
Companies use durability testing results to make improvements in design, select better materials, ensure compliance with standards, and provide durability claims in marketing materials.What is the difference between laboratory and field durability testing?
Laboratory testing uses controlled conditions to simulate real-world stresses, while field testing exposes the product to actual operating conditions in its intended environment.
These FAQs provide a basic understanding of what durability testing entails, its importance, and how it is applied across various products and industries.
Conclusion
Durability testing is an essential element of product development and manufacturing. From jet engines to automobiles, smartphones, and beyond, durability testing helps manufacturers to produce more reliable, higher quality, and longer-lasting products. Building more reliable products leads not only to more profits but to increased consumer satisfaction and public safety.





