SIRIUS® Modular
Modular Data Acquisition (DAQ) System
Torsional and rotational vibrations are quite often a source of issues and faults on the rotating shafts. Our rotational and torsional vibration analysis solution combined with the order tracking analysis solution are perfect tools for troubleshooting rotating shafts, crankshafts, and gears in automotive, industrial, or power-generation applications.
The math module supports any type of sensor. The sensors type can be totally different for both ends of the rotor. SuperCounter technology provides 10 nano seconds resolution of determining rotational angle and speed.
All data, such as reference angle, individual sensor rotational angle, speeds and acceleration, torsional angle, and velocity are readily available for advanced analysis.
Different input filters and rotational DC filters are available as well as a chance to enter the rotational speed ratio for gearbox analysis.
Closely combined with order tracking, advanced data analysis is available based on same angle sensors as the source of frequency,
Every Dewesoft data acquisition system is bundled with award-winning DewesoftX data acquisition software. The software is easy to use but very rich and deep in functionality. All software updates are free forever with no hidden licensing or yearly maintenance fees.
Enjoy our industry-leading 7-year warranty. Our data acquisition systems are made in Europe, utilizing only the highest build quality standards. We offer free and customer-focused technical support. Your investment into the Dewesoft solutions is protected for years ahead.
And we're confident you'll love it too! But don't just take our word for it. Get hands-on with a demo unit, completely free of charge. No strings attached, just real data. Reach out to your local Dewesoft team and get your demo unit now!
It includes everything you need for advanced data acquisition and common signal processing — no maintenance fees, no contracts. You buy it, you own it. All future updates? Free forever. And the best part? Analysis seats are unlimited and free. Once the data is recorded, anyone can download our software to review and analyze your data — no license needed.
Dewesoft is 100% owned by employees who believe in what we do — and love doing it. We’re in this with heart, passion, and long-term commitment. What does that mean for you? Our core value — caring for our customers — isn’t going anywhere. We’re here for the next 100 years, protected from outside acquisitions. Your investment in our technology is safe, supported, and future-proof.
At Dewesoft, quality isn't just a promise — it's a core value. Our products are 100% designed, developed, and manufactured in-house, right in the heart of the European Union. From precision machining and PCB manufacturing to final assembly and software development — we do it all ourselves, to the highest ISO standards. We're proud to support local production and take social responsibility seriously.
At Dewesoft, quality is more than just a word — it's a commitment. That's why our products come with an industry-leading 7-year warranty. It's just one more way we protect your investment and give you peace of mind for the long run.
Torsional vibrations are angular vibrations of an object, typically a shaft along its axis of rotation. They are mechanical vibrations caused by time-alternating torques which are superimposed on the otherwise steady running speed of a rotating shaft. In automotive engineering torsional vibration is primarily driven by fluctuations in engine power output.
Torsional vibrations are evaluated as the variation of rotational speed within a rotation cycle. RPM variations are typically induced by a rough driving torque or a varying load.
Rotational vibration is simply the dynamic component of the rotational speed. If we measure the rotational speed of the shaft with high precision, we will notice that we get a high deviation of rotational speed in some regions of the run-up. This is caused by the angular vibration crossing the angular natural frequency of the shaft. It is calculated by cutting off the DC component of the rotational speed or the rotation angle
The level of torsional vibration is influenced by a number of parameters, such as material properties and operating conditions such as temperature, load, RPM, etc.
Our data acquisition systems for collecting data for torsional vibration analysis offer very flexible channel configurations and easy connection of sensors. With advanced TEDS sensors support and integrated smart DAQ technologies, the sensor setup and channel configuration will be instant and you will be able to start measuring in minutes.
The award-winning Dewesoft X data acquisition software already includes a predefined display for torsional vibration. Just run your machine and the data and results will start displaying in real-time on the screen. Visual displays are freely configurable and you can change your display at any time online or offline. Connect a simple web camera and have synchronized video of your measured machine next to your measured data.
Simple built-in reporting tools and extensive file format export functionalities will enable you to create quick PDF reports or export data to Excel, Matlab or other supported SW packages for further analysis, if needed.
Torsional and rotational vibration can be measured with either an encoder sensor (up to 3600 pulses per revolution) or a special sensor (CA-RIE-360/720) that has a lower resolution (up to 720 pulses per revolution) but is much less sensitive to vibrations that could damage standard encoders.
Some very typical sensors are already predefined in the Dewesoft X DAQ software. However, if your type is not listed, you can define your own sensor in the sensor editor. Note, that for the torsional vibration module the sensor has to be either an Encoder or a CDM type.
A variety of angular sensors is supported:
Encoders
CDM with/without zero pulses (Geartooth)
Zebra tape sensor (tacho and auto-gap detection)
Sensors with missing teeth (e.g. 60-2)
Dewesoft data acquisition systems utilize a patented and registered trademark technology called SuperCounter®.
Counter inputs can measure the RPM and angle of rotating machines. In comparison to standard counters, which only output integer numbers one sample later (e.g. 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4), the Dewesoft SuperCounter inputs are able to extract accurate values like 1.37, 1.87, 2.37, etc. fully synchronized for time and amplitude.
This is done by measuring the exact time of the rising edge of the signal with an additional counter. Our SuperCounter inputs work on a 102.4 MHz time base, independent of the current analog sampling rate.
Counter inputs are fully synchronized with analog, CAN bus, and other data sources to enable easy applications like balancing, order tracking, and torsional vibrations.
Dewesoft X torsional vibration module automatically calculates several different parameters. The calculations can be done either online in real-time or offline on the saved RAW data.
Rotational angle: filtered angle value of vibration.
Rotational velocity: filtered velocity vibration value.
Torsional angle: the Dynamic torsional angle that is the angle difference from sensor 1 to sensor 2.
Torsional velocity: difference in angular velocity from sensor 1 to sensor 2.
X-axis reference angle: the reference angle, which is always from 0 to 360 and can be used as a reference in angle-based XY diagrams.
Frequency: in the RPM units.
The input filter is needed to prevent glitches and spikes in the digital encoder pulse signal. It can be set from 100ns to 5us, and the optimal setting is calculated.
The rotational DC-filter needs to be set to cut the DC component of the RPMs. We need to set the filter to include all wanted frequencies, but not too low, or else we will have static DC deviations on the output signal. It can be set from 0.1 to 10 Hz. You have to ensure that your lowest RPM is not filtered out!
Centered mounting is very important. Off-center mounting and unsteady pulses from the encoder can be compensated in Dewesoft X using the reference curve.
However, it is required that the load must be removed from the engine - it must be free-running. Otherwise, you would also cancel out the vibrations you want to analyze. When the machine is running at idle speed with no real torsional vibration, press the “Set” button.
See and browse related and compatible data acquisition products.
Modular Data Acquisition (DAQ) System
Portable 4-Channel Sound and Vibration Analyzer
Portable Data Acquisition (DAQ) Systems
8-Channel Universal Data Acquisition System
8-Channel USB Data Acquisition (DAQ) System
Award-Winning Data Acquisition and Digital Signal Processing Software
See and browse related and compatible testing solutions.
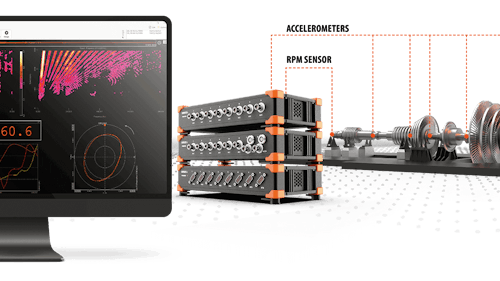
Noise and vibration analysis for rotating and reciprocating machinery
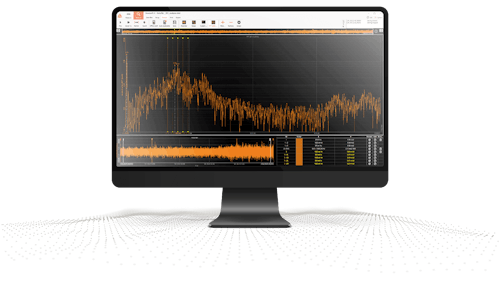
Vibration and frequency analysis with a Fast Fourier transform