IOLITE® Modular
Modular Industrial Data Acquisition (DAQ) Systems
Dewesoft data acquisition systems are used in structural health and seismic bridge monitoring projects ranging from structural mechanics to continuous monitoring of large, complex bridge structures.
The monitoring systems provide distributed, high-channel-count and remote monitoring for highway overpasses, roads, buildings, and bridges. We provide a total solution from DAQ systems and data loggers to sensors and monitoring software.
Dewesoft bridge monitoring solution offers complete and highly accurate data acquisition systems, data loggers (including wireless dataloggers), and the possibility to connect all necessary sensors that are used info structural health monitoring projects.
Dewesoft DAQ devices are designed to be distributed under any condition. EtherCAT technology allows devices to be placed near the sensors and connected with a single cable for power, data, and synchronization. The cable can span up to 100m between DAQ nodes or virtually unlimited using EtherCAT to fiber optic converters.
Input amplifiers offer support for any strain gauge sensor, low-frequency accelerometer sensors for seismic activity monitoring, temperature, and weather factors.
All data channels are synchronized well below microsecond accuracy, required for deep structural analysis.
With dynamic ranges up to 160dB, our customers are claiming they can see fish hitting the structure.
From extremely rugged IP67 units with very high dynamic range to cost-effective solutions offer a tailored approach for virtually any structure with the possibility to monitor and analyze thousands of data points.
DewesoftX software offers real-time diagnosis, pre-processing, and data reduction with powerful math. A wide variety of storage options are possible with powerful visualization choices.
Using DewesoftX, data is available in a wide variety of formats, from exported data to live OPC UA interface or modern cloud data services.
Use recorded time data to estimate modal models. With OMA the dynamics of the structural vibrations can be determined directly from the sensor input data via the Dewesoft ARTeMIS OMA software.
The entire system can be remotely operated offering triggered storing, alarms, and other monitoring features with capabilities to store data locally or at distant remote locations.
Every Dewesoft data acquisition system is bundled with award-winning DewesoftX data acquisition software. The software is easy to use but very rich and deep in functionality. All software updates are free forever with no hidden licensing or yearly maintenance fees.
Enjoy our industry-leading 7-year warranty. Our data acquisition systems are made in Europe, utilizing only the highest build quality standards. We offer free and customer-focused technical support. Your investment into the Dewesoft solutions is protected for years ahead.
And we're confident you'll love it too! But don't just take our word for it. Get hands-on with a demo unit, completely free of charge. No strings attached, just real data. Reach out to your local Dewesoft team and get your demo unit now!
It includes everything you need for advanced data acquisition and common signal processing — no maintenance fees, no contracts. You buy it, you own it. All future updates? Free forever. And the best part? Analysis seats are unlimited and free. Once the data is recorded, anyone can download our software to review and analyze your data — no license needed.
Dewesoft is 100% owned by employees who believe in what we do — and love doing it. We’re in this with heart, passion, and long-term commitment. What does that mean for you? Our core value — caring for our customers — isn’t going anywhere. We’re here for the next 100 years, protected from outside acquisitions. Your investment in our technology is safe, supported, and future-proof.
At Dewesoft, quality isn't just a promise — it's a core value. Our products are 100% designed, developed, and manufactured in-house, right in the heart of the European Union. From precision machining and PCB manufacturing to final assembly and software development — we do it all ourselves, to the highest ISO standards. We're proud to support local production and take social responsibility seriously.
At Dewesoft, quality is more than just a word — it's a commitment. That's why our products come with an industry-leading 7-year warranty. It's just one more way we protect your investment and give you peace of mind for the long run.
1 - Acceleration and inclination measurement: Dewesoft IOLITEicw-3xMEMS-ACC-INC a Triaxial MEMS accelerometer and static inclinometer with EtherCAT interface, 8 g measurement range.
2 - Displacement measurement: Dewesoft IOLITEicw-3xMEMS-ACC a Triaxial MEMS accelerometer that precisely measures displacement by integrating acceleration twice.
3 - Static Strain measurement: An embedded vibrating wire strain gauge designed to be embedded into concrete structures for monitoring static strain of concrete.
4 - All in one weather station: The weather station provides a measurement of relative humidity, temperature, wind speed & direction, brightness, and twilight.
5 - Dynamic strain gauge: Bolt-on dynamic strain gauge designed to be mounted on the structure.
6 - IOLITEicw-3xMEMS-ACC: Triaxial MEMS accelerometer with EtherCAT interface and 8 g measurement range.
7 - Asphalt temperature measurement
8 - Corrosion sensor
0 - Air temperature and humidity measurement
10 - IOLITE - From single-channel to multi-channel distributed data acquisition devices capable to read data from accelerometers, dynamic strain gauges, thermocouples, RTDs, weather stations, potentiometers, etc.
11 - VW Wireless data logger - For reading the data from vibrating wire sensors.
12 - OBSIDIAN - An embedded data acquisition system and data logger all in one.
Dewesoft Data Acquisition systems with their wide range of analog and digital inputs, offer support for almost any kind of 3rd party sensor used in Structural Health Monitoring.
All EtherCAT compatible devices (IOLITE, IOLITEicw, KRYPTON) can be connected to the same network giving the possibility to build a virtually unlimited channel chain by using a single cable delivering power, synchronization, and data. The whole EtherCAT chain is synchronized to 1us no matter the distance. Node-node distances can be up to 100m.
All the raw data from data acquisition devices are collected and processed by measurement units running the DewesoftX data acquisition software. Processed data is sent over the TCP/IP network to the factory or cloud server. Data can be accessed and viewed on the client PC or stored in the time series database (Historian) and served to SCADA systems or Cloud Software using standard interfaces such as OPC/UA or XCP to truly support Industry 4.0 applications.
Bridges endure constant stress from traffic loads, wind forces, temperature changes, and environmental conditions. Understanding their structural behavior is essential for ensuring long-term safety and performance. Dewesoft provides a complete solution for bridge modal analysis, including:
Operational Modal Analysis (OMA),
Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA), and
Operating Deflection Shapes (ODS),
enabling engineers to assess structural integrity with ease.
OMA is ideal for monitoring bridges in real-world conditions without requiring controlled test excitations. By measuring the bridge’s natural response to ambient loads such as traffic or wind, Dewesoft ARTeMIS OMA software extracts natural frequencies, damping ratios, and mode shapes with high accuracy. Unlike ODS analysis, OMA removes external force influences, providing unbiased modal information that helps detect early signs of structural issues.
For detailed structural assessment, EMA is used to excite the bridge structure using impact hammers or shakers, allowing engineers to directly measure input forces and responses. This controlled testing provides valuable data for validating numerical models, identifying structural weaknesses, and optimizing bridge designs. Dewesoft’s synchronized DAQ systems ensure high-precision measurements with seamless integration into modal testing software for detailed analysis.
ODS analysis is an intuitive method for visualizing how different parts of a bridge move under operational conditions. By measuring vibrations at various points on the structure, Dewesoft ODS analysis tools help engineers pinpoint areas of excessive movement, resonance issues, or potential structural weaknesses. ODS is a powerful complement to OMA and EMA, providing a clear representation of real-world bridge behavior.
Dewesoft’s bridge monitoring solutions are designed to be cost-effective, quick to set up, and scalable for both temporary assessments and long-term monitoring. Our versatile DAQ systems seamlessly integrate with ARTeMIS OMA and other modal analysis tools, allowing users to acquire vibration data, open DXD files directly, and run advanced analysis with minimal effort.
Learn more: Modal testing and modal analysis solution page.
Dewesoft provides very rugged data acquisition units that can work flawlessly in a wide temperature range, under big stress, and even in very humid and wet environments.
Data acquisition units can easily be distributed so you can place them close to the sensor placed on the structure. This means shorter sensor cabling which increases signal quality, and decreases the chances of cabling errors and cabling cost. DAQ systems can be distributed down to a single channel.
EtherCAT protocol provides a connection of up to 100 meters between DAQ nodes. Single power is used for data, power, and synchronization. This can be further expanded using EtherCAT to Fiber Optic converters.
DewesoftX software offers easy and flexible configurations for your data flow. You can store data locally near the structure itself, or use any of the standard interfaces like OPC UA to send and store data remotely in the cloud or database. There is really no restriction on how to set up your data flow.
Our flexible licensing allows you to connect an unlimited number of view clients to monitor data in real-time without any additional cost.
The Historian software package provides a time-series database for long-term data storage. The database can be either located locally, on the remote server, or in the cloud. The solution is based on the InfluxDB time-series database open source project.
Historian provides several useful features for your historic data:
Raw and reduced data: while raw data is always stored on the measurement unit for an in-depth analysis, a Historian takes the role of long-term reduced data storage in the cloud database.
Data safety and retransmit: if the connection between the measurement hardware and the database is lost, the data is safely stored locally on the measurement unit and then retransmitted to the database when the connection is available.
Trending and Analysis: Historical data can always be recalled and loaded from the Historian database and used for trend analysis as well as for in-depth analysis and root cause identification.
Dewesoft structural monitoring solutions can be tailor-made and configured for all sorts of structural health monitoring applications. Some of the common applications we are delivering:
Bridge health monitoring
Overpass monitoring
Dam monitoring
Monitoring during construction
High-rise building monitoring
Dewesoft Structural Health Monitoring projects have been successfully applied in many locations and are providing high-fidelity data for decision-making. Here are just some of the reference case studies:
See full list of Dewesoft case-studies here.
See and browse related and compatible data acquisition products.
Modular Industrial Data Acquisition (DAQ) Systems
Low-Noise Triaxial MEMS Accelerometers and Inclinometers
Data logger and embedded data acquisition system
Rugged EtherCAT Data Acquisition (DAQ) System
Small, Rugged, IP67 Datalogger and Processing Computer
Time-Series Database for Long-Term and Permanent Monitoring Applications
Award-Winning Data Acquisition and Digital Signal Processing Software
See and browse related and compatible testing solutions.
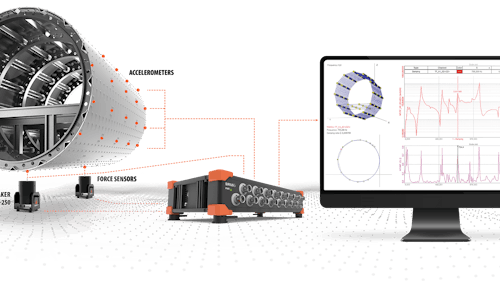
Structural dynamics testing and analysis solution
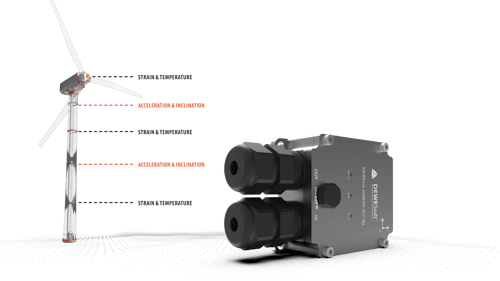
Structural Health Monitoring and Condition Monitoring of Wind Turbines